Cloud Computing
In recent years, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force in the world of technology, revolutionizing the way businesses and individuals store, access, and manage their data. The concept of cloud computing revolves around the idea of delivering on-demand computing resources over the internet, including storage, processing power, and software applications. This paradigm shift has had a profound impact on various industries, from small startups to large enterprises, offering numerous advantages that have reshaped the digital landscape.
Some benefits
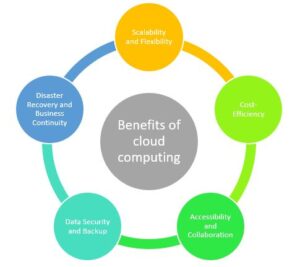
Scalability and Flexibility:
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Organizations can quickly scale up or down their computing resources based on demand. Whether it’s a sudden surge in website traffic or the need to process large amounts of data, cloud computing allows businesses to easily adjust their infrastructure to meet changing needs. This flexibility enables organizations to be more agile and responsive to market demands, ultimately saving time and resources.
Cost-Efficiency:
Cloud computing eliminates the need for substantial upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead of purchasing and maintaining physical servers, businesses can pay for cloud services on a subscription or usage basis. This pay-as-you-go model significantly reduces capital expenses. Moreover, cloud computing reduces the costs associated with managing and maintaining data centers, such as cooling, power consumption, and IT personnel. By only paying for the resources they actually use, businesses can achieve cost-efficiency and allocate their budgets more effectively, leading to significant savings in the long run.
Accessibility and Collaboration:
One of the key advantages of cloud computing is the convenience and universal access it provides. Cloud services allow users to access their data and applications from any location and device with an internet connection. This accessibility promotes seamless collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location. Multiple individuals can work on the same document simultaneously, making real-time collaboration easier than ever before. Cloud-based collaboration tools enhance productivity and efficiency, particularly in today’s globally distributed workforce, as employees can work together seamlessly and share information in real-time.
Data Security and Backup:
Cloud service providers prioritize the security of data stored in the cloud. They invest heavily in robust security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats. Cloud providers employ advanced encryption techniques, authentication protocols, and regular security updates to ensure the safety and integrity of the data. Additionally, cloud storage acts as a backup solution. By storing data in the cloud, businesses reduce the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or human errors. Cloud providers often offer data redundancy across multiple locations, ensuring data availability and reliability.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. In traditional IT infrastructure, implementing disaster recovery plans can be complex and costly. However, cloud providers often have built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure the availability of services in the event of a failure or disaster. Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions allow businesses to quickly recover their data and systems, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. This resilience is particularly crucial for organizations that rely heavily on their IT infrastructure and cannot afford prolonged disruptions.
Other Important Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- Increased agility and scalability
- Mobile access and remote work capabilities
- Cost savings on hardware and infrastructure
- Rapid deployment of new applications and services
- High availability and reliability
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing:
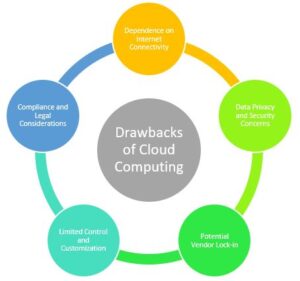
Dependency on Internet Connectivity:
One of the primary drawbacks of cloud computing is its reliance on internet connectivity. Without a stable and reliable internet connection, users may experience difficulties accessing their data or utilizing cloud-based services. This dependency on the internet introduces a level of vulnerability, as downtime or disruptions in connectivity can disrupt business operations. While internet connectivity is generally widespread, occasional outages or slowdowns can still occur, affecting cloud accessibility. Organizations must consider backup internet connections or alternative plans to mitigate the impact of internet connectivity issues.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns:
While cloud providers implement robust security measures, concerns over data privacy and security persist. Storing data on remote servers raises questions about who has access to that data and how secure it truly is. Organizations that deal with highly sensitive or regulated data may hesitate to store it in the cloud due to compliance requirements or the fear of data breaches. Adequate due diligence and careful selection of reputable cloud service providers can help mitigate these concerns to a large extent. It’s crucial for businesses to thoroughly understand the security measures and compliance certifications offered by their cloud providers and ensure they align with their specific needs.
Potential Vendor Lock-In:
When an organization migrates its infrastructure and applications to the cloud, it may become reliant on a specific cloud provider’s technologies, tools, and APIs. This dependency can create a potential vendor lock-in situation, where switching to another provider or bringing operations back in-house becomes challenging and costly. Businesses must carefully evaluate their options and choose providers that offer interoperability and data portability to avoid vendor lock-in scenarios. Using open standards and APIs can provide more flexibility and make transitioning between cloud providers or hybrid cloud environments easier.
Limited Control and Customization:
Cloud computing often involves relinquishing some control over infrastructure and software customization. Organizations may find themselves limited by the capabilities and configurations provided by their cloud service provider. Customizing certain aspects of the infrastructure or applications to fit specific needs may be challenging or impossible. This lack of control can pose challenges for businesses with unique requirements or those operating in highly regulated industries that demand extensive customization. Organizations must carefully assess their needs and evaluate whether the available customization options offered by cloud providers align with their requirements.
Compliance and Legal Considerations:
Businesses operating in certain industries or geographic regions may face compliance and legal challenges when adopting cloud computing. Data protection regulations and privacy laws may impose restrictions on where certain types of data can be stored or processed. Cloud providers must comply with these regulations, but organizations must also ensure that their chosen cloud provider aligns with the specific compliance requirements they need to meet. It’s crucial to understand the legal and regulatory landscape and work with cloud providers that have a strong track record of compliance and data governance.
Other Important Drawbacks of Cloud Computing:
- Highly depending on internet connectivity
- Potential data security and privacy risks
- Limited control and customization
- Potential vendor lock-in
- Compliance and legal considerations
Conclusion
Cloud computing has undeniably transformed the way businesses and individuals store, access, and manage data, offering numerous benefits and opportunities. The scalability, cost-efficiency, accessibility, and data security provided by cloud computing have revolutionized modern work environments and enabled organizations to adapt to changing market demands more effectively. However, it is crucial to consider the potential drawbacks of cloud computing, such as dependency on internet connectivity, data privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, limited control and customization, and compliance and legal considerations. By carefully assessing these factors and adopting appropriate mitigation strategies, businesses can make informed decisions about adopting cloud computing and leverage its benefits while managing potential risks.
Good job
Well done
Please keep connected with us for such interesting contents.
Well done
Thank for the Update
[…] regular updates, and adaptability to stay ahead of evolving threats in the dynamic landscape of cloud computing. With a well-structured security framework, organizations can confidently embrace the benefits of […]
Nice.
Engaging and informative!
A thorough analysis of AI in marketing tactics is evident.
Share something related to this topic
Thanks for sharing.